Many missionaries work across various countries in Africa, addressing challenges such as drought, soil degradation, and lack of modern farming techniques. They often collaborate with local communities to introduce drought-resistant crops, improved irrigation methods, and sustainable farming practices. Organizations like the Association of Church Development Projects (ACDP) have been active in promoting agricultural development in Africa through missionary efforts. In countries like Honduras and Guatemala, agricultural missionaries have focused on training local farmers in organic farming methods. They have introduced techniques such as composting, crop rotation, and natural pest control to improve soil fertility and reduce dependency on chemical inputs. These efforts have not only increased yields but also enhanced the economic stability of rural communities. In countries like India and Bangladesh, agricultural missionaries have played a crucial role in introducing new farming technologies and practices. They have worked on projects related to water management, high-yield crop varieties, and agricultural diversification. For example, missionaries have promoted the use of solar-powered irrigation systems in remote areas where access to electricity is limited.

Crop: Golden Rice, a genetically modified rice variety enriched with beta- carotene to combat Vitamin A deficiency. 2. Location: Philippines, Bangladesh, and Indonesia. 3. Case Study: The development and promotion of Golden Rice have been pivotal in regions where Vitamin A deficiency is prevalent. Agricultural scientists and organizations like the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) have collaborated with local farmers to cultivate and disseminate this biofortified crop. Despite initial challenges and controversies surrounding GMOs, Golden Rice has shown promise in addressing nutritional deficiencies. Quinoa in South: 4. Crop: Quinoa, a nutrient-dense grain native to the Andean region. 5. Location: Bolivia, Peru, and Ecuador. 6. Case Study: Quinoa's cultivation has surged globally due to its high nutritional value and adaptability to harsh environments. In South America, NGOs and agricultural development organizations have promoted sustainable farming practices for quinoa, benefiting local farmers economically and improving food security. However, concerns about environmental sustainability and fair trade practices have emerged as demand for quinoa increases globally.

Organic Fertilizers:Derived directly from plant or animal sources, such as manures, compost, or bone meal.Also include rock minerals (finely ground limestone and rock phosphate).Nutrients are in lower concentrations but may have a wider range of nutrients.Slow-release: Soil bacteria and fungi convert nutrients into inorganic forms, making them available to plants over time. Advantages:Improve soil structure.Don’t form a crust on the soil.Feed beneficial microbes.Enhance water movement.Enrich the soil.Environmentally friendly.Disadvantages:Cost more than conventional fertilizers.Less concentrated (supply fewer nutrients pound for pound). Chemical (Conventional) Fertilizers:Often called synthetic fertilizers.Go through a manufacturing process.Contain only a few nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, and sometimes micronutrients).Quickly available for plant uptake.May require multiple applications during the growing season.Can form a crust on the soil.Immediate plant nutrition.May leach into waterways if overused.
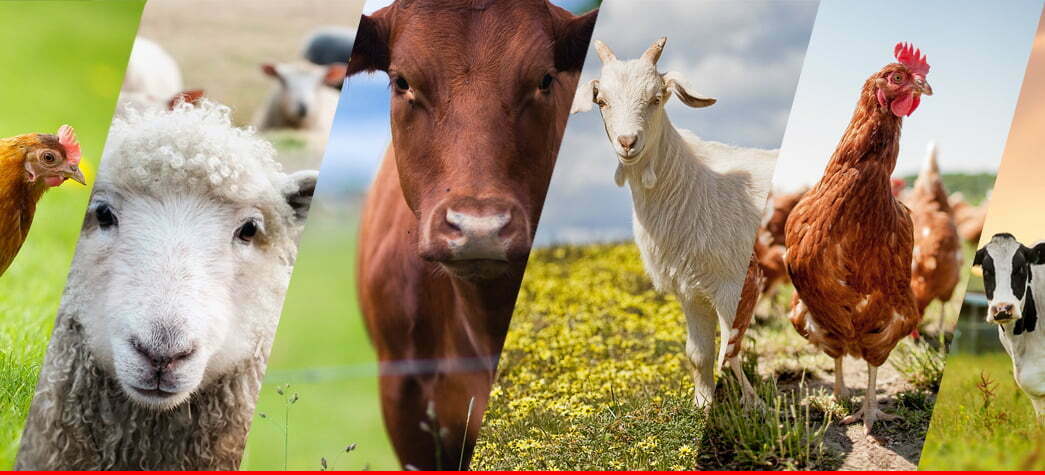

Futures of Livestock and Livestock of the Futures: This case study looks ahead to the future of livestock and food animals. It considers how past traditions of animal husbandry inform our present care of livestock and how these patterns might evolve. The livestock of the past and present include pigs, cattle, sheep, goats, horses, chickens, ducks, geese, farmed salmon, shrimp, and bees. The study explores critical emerging changes and builds five challenging, exploratory scenarios for the future of livestock and food animals, considering health, wellbeing, and sustainability. The Stalwart Family Farm Case Study: The Stalwart Family Farm, located in Maryland, evolved from a small operation to a 300-acre farm. Integrated Fish Farming in Uttar Pradesh, India: This case study focuses on integrated fish farming (IFF) systems in Uttar Pradesh. Poultry Case Study in Oaxaca, Mexico: Entrepreneurs in the central valleys of Oaxaca improved poultry nutrition and yields using poultry feed provided by El Tío. Southeastern Mississippi Poultry and Beef Farm Case Study: This case study features a family-owned 90-acre poultry and beef farm in southeast Mississippi.
2024 Digital Reachall. All rights reserved | Privacy & Policy | Terms & Conditions.